Preconception Health

Family planning should start before a positive pregnancy test. As about 40% of all pregnancies worldwide are unplanned, preconception health is important for everyone of reproductive age, both for women and their partners.
Pregnancy & Maternal Health

Good-quality antenatal care is one of the most effective ways to prevent pregnancy complications. It provides possibilities for risk factors to be identified and possible health consequences to be prevented or treated.
Nutrition

A balanced diet during your pregnancy is important not just for the mother but even more so for the baby‘s healthy growth and development into adulthood. 43.9% of pregnant women worldwide have limited access to high-quality foods.
Family Support

Working with families expecting a baby will harness the power of parents, particularly those from low-income and disadvantaged backgrounds, and ultimately improve the life chances of children.
Premature Birth
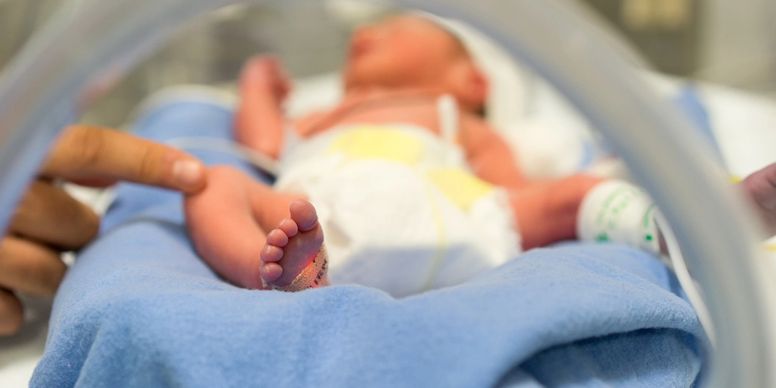
1 in 10 pregnancies globally finish too early. Three-quarters of them could be saved with current, cost-effective interventions. Many preterm babies face a lifetime of disabilities, including learning disabilities and vision and hearing problems.
Loss & Grief

No parent is prepared for the loss of a child. Parents are simply not supposed to outlive their children. There are various reasons that cause grief and loss, including ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, molar pregnancy, neonatal death, and stillbirth.
Postnatal Depression & Anxiety

Maternity blues are common. A new mother feels down and tearful in the week after her baby is born. Postpartum depression & anxiety, however, is a more debilitating and longer-lasting condition and is characterised by despondency, tearfulness, and more intense feelings of inadequacy, guilt, anxiety, and fatigue, as well as a disturbing lack of feeling for the baby.
Standards for Infant Care

Creating a policy framework that serves as a reference for the development and implementation of binding standards and guidelines on a national and international level is of paramount importance for well-functioning societies. When put into practice, the standards ought to ensure quality, equity, and dignity in maternal and infant care.
Breastfeeding

Breastmilk provides the best nutrition for healthy infant development as well as increasing the bonding between the mother and the baby. Breastfeeding is not always easy at the start, but with the help of the attending health provider, self-belief, and support from the surrounding environment, breastfeeding is certain to become an enjoyable experience.
Birth Defects
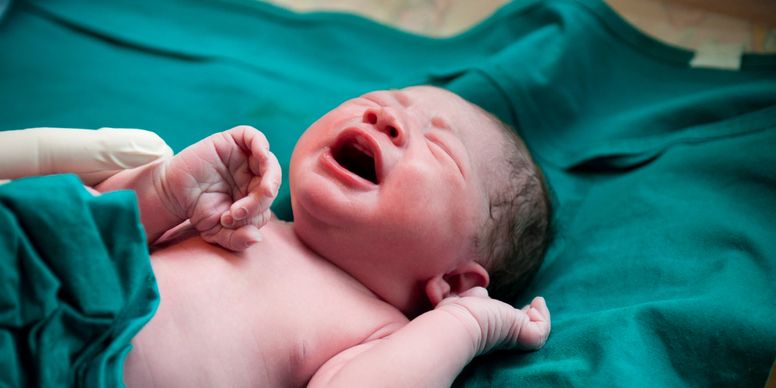
Birth defects are health conditions that are present at birth. They change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body and can cause problems with the overall health of how the body develops or works. If an infant is born with a birth defect or other health condition, they may need special care at birth and later in life.
Infant Health & Care
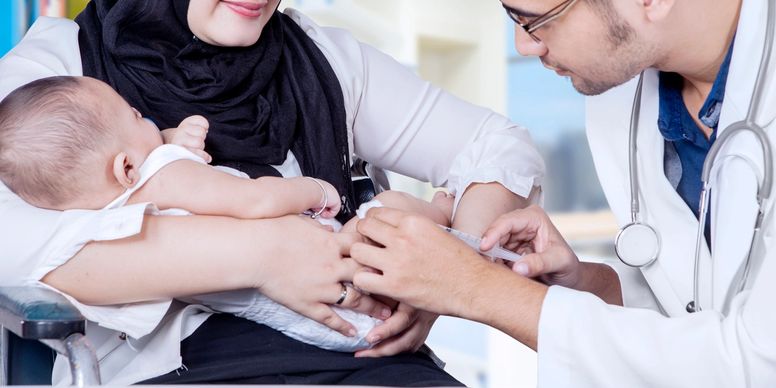
This includes a large framework of activities to ensure the child is developing normally, including new-born screening tests, sleep safety and protection from dangers at home, medical check-ups, vaccinations, and other checks that certify that the child is meeting developmental milestones.
Family-Friendly Public Policies

Family-friendly policies are public policies that help to balance and benefit both work and family life and typically provide three types of essential resources needed by parents and carers of young children: time, finances, and services.
Development Disabilities

There are four main types of developmental disorders: nervous system disabilities, sensory-related disabilities, metabolic disabilities, and degenerative disorders. Children with disabilities might have a hard time letting others know their wants and needs and taking care of themselves. It could take longer for them to learn to speak, walk, dress, or eat without help, and they could have trouble learning in school.
Neglect

A developing child requires proper nutrition, protection, and regulation for healthy attachment. Children who experience neglect are often malnourished. They demonstrate a lack of emotional regulation and difficulty distinguishing emotions. Low self-esteem and low self-worth are also consequential for children who suffer from neglect as well as poor cognitive and academic development.
Childhood Trauma

Childhood trauma is a serious adverse childhood experience that might include abandonment, sexual abuse, and physical abuse, parent or sibling is treated violently, or there is a parent with a mental illness. These events have profound psychological, physiological, and sociological impacts and can have negative, lasting effects on health and well-being.
Poverty, Hunger & Homelessness

Children who grow up impoverished often lack the food, sanitation, shelter, health care, and education they need to survive and thrive. The consequences are grave. Poorer children are at greater risk for negative outcomes such as poor academic achievement, school dropout, abuse and neglect, behavioural and socioemotional problems, physical health problems, and developmental delays.
Quality Education

The progress towards ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education is very slow. In 2030, over 200 million children will be out of school. In low-income countries, the school completion rate is only 34%, in only 20% of households. School closures during COVID-19 kept 90% of the pupils out of school, leaving 500 million without facilities for remote education. 130 million girls still have no access to school or education.
